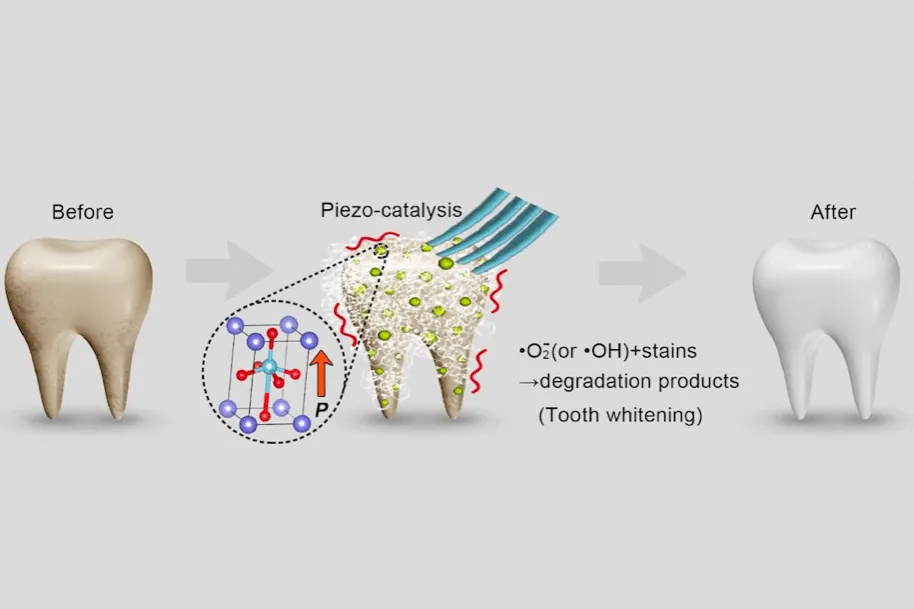
What is Thin Enamel
Thin enamel is a condition where the outer protective layer of your teeth, known as enamel, is thinner than usual. Enamel is the hardest substance in the human body and protects the underlying dentin and the sensitive inner pulp. When enamel is thin, the dentin, which is naturally more yellow, becomes more visible, making teeth appear less white. This condition can be caused by genetics, excessive acid exposure (from certain foods or conditions like GERD), teeth grinding, or aggressive brushing. Thin enamel makes teeth more susceptible to sensitivity, cavities, and even damage from whitening treatments. Understanding this condition is crucial for anyone considering teeth whitening, as it directly impacts the safety and effectiveness of the procedure.
Understanding the Risks of Teeth Whitening with Thin Enamel
Teeth whitening treatments can pose several risks for individuals with thin enamel. The primary concern is increased tooth sensitivity. Whitening agents, such as hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, work by penetrating the enamel to break down stains. However, if the enamel is thin, these agents can more easily reach the dentin and the nerves inside the tooth, leading to heightened sensitivity. Furthermore, the chemicals can cause irritation to the gums and soft tissues of the mouth. In severe cases, aggressive whitening can even weaken the enamel further, increasing the risk of damage, such as chipping or cracking. It’s essential to be aware of these risks before undergoing any whitening procedure.
Increased Sensitivity
One of the most common side effects of teeth whitening with thin enamel is increased tooth sensitivity. This sensitivity can manifest as sharp, shooting pains when consuming hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and drinks. The whitening agents penetrate the enamel and reach the dentin, stimulating the nerves and causing discomfort. The thinner the enamel, the more pronounced the sensitivity tends to be. This sensitivity can last for a few days or even weeks after the whitening treatment. Proper precautions, such as using desensitizing toothpaste before and after the procedure, can help mitigate this effect. However, individuals with pre-existing sensitivity issues or very thin enamel should proceed with extreme caution.
Potential for Irritation
Whitening products can also cause irritation to the soft tissues of the mouth, including the gums. This can result in redness, swelling, and soreness. The whitening agents, particularly those with higher concentrations of peroxide, can irritate the delicate gum tissues. This irritation is often more pronounced in individuals with thin enamel because the enamel provides less protection. Furthermore, ill-fitting whitening trays can exacerbate the problem by allowing the whitening agent to come into direct contact with the gums. It’s essential to ensure that any whitening treatment is performed under professional supervision to minimize the risk of irritation and to address any issues promptly.
Risk of Damage
In the most severe cases, teeth whitening can potentially damage thin enamel, increasing the risk of chipping, cracking, or even erosion. The whitening agents can weaken the enamel, making it more vulnerable to damage from everyday wear and tear or biting and chewing. Individuals with existing enamel erosion or structural problems are at a higher risk. It is critical to carefully assess the condition of the enamel before undergoing any whitening treatment. A dentist can evaluate the enamel thickness and overall health, recommending alternative or modified treatments that are safer. If the enamel is significantly thin or compromised, it may be best to avoid whitening altogether or explore less aggressive options.
Top 5 Facts about Teeth Whitening for Thin Enamel
Fact 1 Impact of Thin Enamel on Whitening
Thin enamel significantly affects the outcome and safety of teeth whitening. Because the enamel layer is the outer protective layer, thinner enamel means that whitening agents can more easily penetrate to the dentin, which is the layer beneath the enamel. This can lead to increased sensitivity and potential damage to the teeth. Moreover, the whitening effect may be less noticeable if the underlying dentin is more yellow due to the reduced enamel coverage. Therefore, individuals with thin enamel should approach teeth whitening with caution and consult with a dentist to determine the most appropriate and safest method. The dentist can assess the enamel thickness and recommend treatments that minimize risks and maximize results.
Fact 2 Choosing the Right Whitening Method
Selecting the appropriate whitening method is crucial when you have thin enamel. Over-the-counter whitening products, such as strips and gels, often contain high concentrations of whitening agents and can be too harsh. Professional whitening treatments offered by a dentist offer greater control over the process. Your dentist can customize the treatment to your specific needs, using lower concentrations of whitening agents or applying protective measures to minimize sensitivity. For thin enamel, gentle whitening options, such as custom-made trays with lower-concentration peroxide gels or stain removal with polishing, might be more suitable and safer. Always consult a dentist to determine the most appropriate and safe method.
Fact 3 Ingredients to Avoid
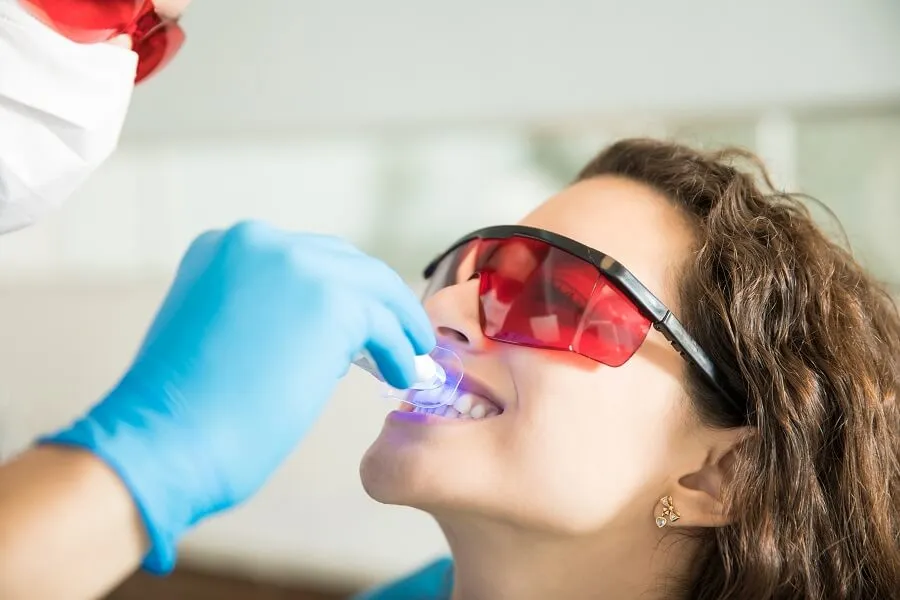

When you have thin enamel, it’s important to be mindful of the ingredients in teeth whitening products. Avoid products containing high concentrations of hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, as these are the primary bleaching agents that can cause sensitivity and damage. Look for products with lower concentrations, or consider alternatives such as whitening toothpastes with abrasive ingredients designed to remove surface stains, but which are less likely to penetrate the enamel. Always check the product label and consult with your dentist before using any whitening product, especially if you have thin enamel or any existing dental issues. Ingredients like alcohol or strong flavors can also be irritating.
Fact 4 Importance of Professional Advice
Seeking professional advice from a dentist is paramount when considering teeth whitening with thin enamel. A dentist can assess the condition of your teeth, including the thickness and integrity of the enamel, and identify any underlying issues that might affect the treatment. They can recommend the safest and most effective whitening methods based on your individual needs. Furthermore, a dentist can offer pre- and post-whitening care instructions to minimize sensitivity and protect the enamel. Regular dental check-ups allow the dentist to monitor your oral health and address any concerns promptly. The expertise of a dental professional is crucial for achieving the desired results safely.
Fact 5 Post-Whitening Care
Proper post-whitening care is essential for individuals with thin enamel. After whitening, teeth can be more sensitive and susceptible to staining. Avoid consuming highly pigmented foods and drinks, such as coffee, tea, red wine, and berries, for at least a week or two after the treatment. Use a desensitizing toothpaste containing ingredients like potassium nitrate to reduce sensitivity. Maintain a good oral hygiene routine, including brushing twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and flossing daily. Consider using a remineralizing toothpaste to help strengthen the enamel. Regular dental check-ups are also crucial to monitor the health of your teeth and address any issues promptly.
Safe Teeth Whitening Methods for Thin Enamel
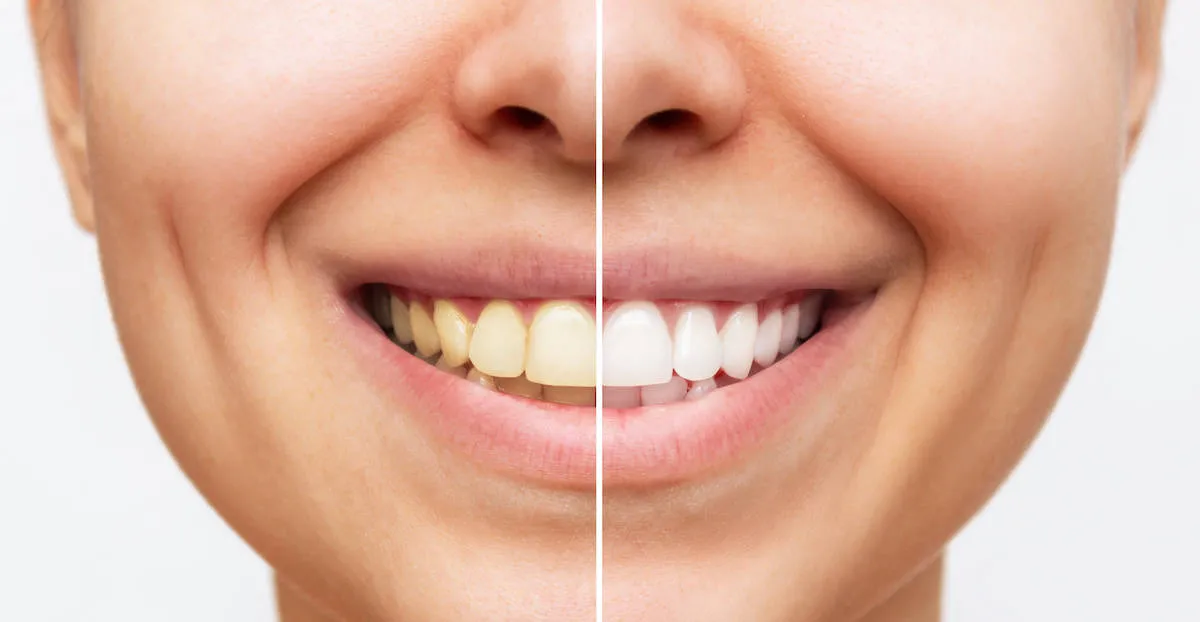

Professional Whitening Options
Professional whitening treatments are generally safer for thin enamel because they are administered under the supervision of a dentist. Your dentist can customize the treatment by using lower concentrations of whitening agents and applying protective measures to minimize sensitivity. They can also monitor the process closely and make adjustments as needed. Some professional options include in-office whitening treatments, which offer immediate results, and custom-made whitening trays, which allow for a more controlled and gradual approach. Professional whitening often includes desensitizing treatments to reduce discomfort. Consulting with a dentist is the best way to determine the most suitable and safe professional whitening option for your specific needs.
At-Home Alternatives
When you have thin enamel, carefully consider at-home whitening options. Avoid over-the-counter products with high concentrations of peroxide. Instead, consult your dentist about using custom-made trays with lower-concentration peroxide gels, which can be more controlled and gentler on your teeth. Whitening toothpastes containing mild abrasive agents, designed to remove surface stains, can also be a safer alternative. However, even with these alternatives, it’s important to follow your dentist’s recommendations and be mindful of any sensitivity. Always consult with your dentist before starting any at-home whitening treatment to ensure it is safe for your individual oral health.
Tips for Protecting Thin Enamel During Whitening
Consult a Dentist First
Before undergoing any teeth whitening treatment, consulting a dentist is paramount, particularly if you have thin enamel. A dentist can evaluate the thickness and condition of your enamel and identify any potential risks. They can recommend the safest and most effective whitening methods based on your individual needs and oral health. During the consultation, the dentist can also discuss pre- and post-whitening care instructions, such as using desensitizing toothpaste or avoiding certain foods and drinks, to minimize any discomfort and protect the enamel. A professional assessment ensures that you make an informed decision and receive a tailored approach to teeth whitening.
Use a Remineralizing Toothpaste
Using a remineralizing toothpaste can help protect and strengthen thin enamel during and after teeth whitening. These toothpastes contain ingredients like fluoride and hydroxyapatite, which help replenish minerals in the enamel, making it more resistant to acid attacks and damage. Remineralizing toothpaste can also reduce tooth sensitivity, a common issue with thin enamel. Incorporating this type of toothpaste into your daily oral hygiene routine can help maintain the health of your enamel and minimize the risks associated with teeth whitening. Consult your dentist to choose a remineralizing toothpaste that best suits your needs.
Maintain a Proper Oral Hygiene Routine
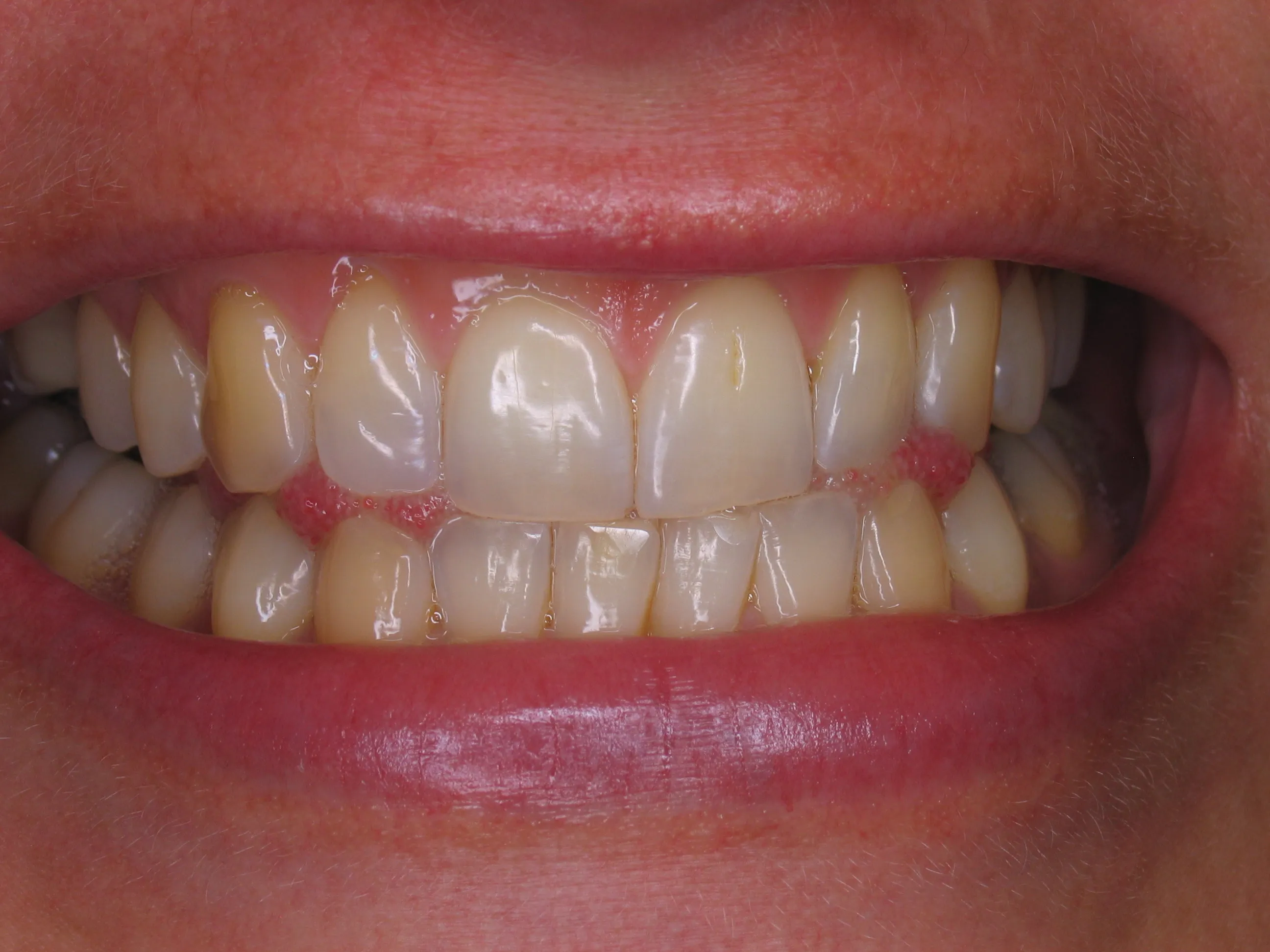
Maintaining a proper oral hygiene routine is crucial for protecting thin enamel during and after teeth whitening. This includes brushing your teeth gently twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and flossing daily to remove plaque and food particles. Avoid aggressive brushing, which can wear down the enamel. Consider using a toothpaste specifically designed for sensitive teeth, which can help reduce discomfort. Rinsing with an alcohol-free fluoride mouthwash can also strengthen the enamel and protect against cavities. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are essential for maintaining optimal oral health and addressing any issues promptly. A good oral hygiene routine is fundamental to protecting your teeth and maintaining the results of teeth whitening.